Certificate error on blocked domains when using OpenDNS
OpenDNS helps in blocking malware sites by not resolving malware domains to the actual IP address hosting the malware. Instead they resolve to an OpenDNS page indicating “This domain is blocked due to …". If you are opening a non-SSL page, this would work as described. However, when attempting to browse a malware page via HTTPS, the web browser will show a certificate error instead. Read on to know the reason and solution.
What is OpenDNS
If you have not heard of them, they are a public DNS resolver service provider much like Google DNS except that OpenDNS blocks malware sites and domains that fall under categories that you wish you block. OpenDNS is owned by Cisco.
Why is my browser showing certificate error instead of malware alert page
This is because the malware domain that you are trying to browse is hosted on a secure server via HTTPS protocol. When browsing a HTTPS page, your web browser will attempt to validate the signature of the certificate. Failure which, your web browser will simply complain of certificate errors.
In order for OpenDNS to notify you that you are attempting to browse a malware domain, it needs to resolve the malware domain to an IP address of OpenDNS page informing you of the malware instead of resolving to the actual malware page. This IP address diversion works. However, OpenDNS website produces a certificate of their own instead of one that belongs to the malware domain.
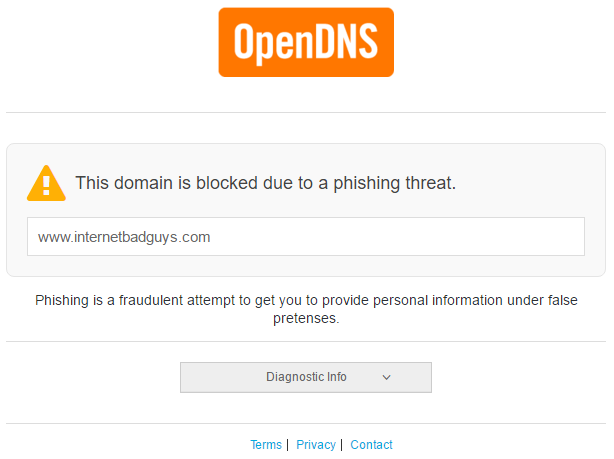
You can test this behaviour safely by visiting OpenDNS mock phishing website. You should be seeing certificate error.
The solution
Before we begin, please read on how to configure OpenDNS DNS-O-Matic so that OpenDNS is aware of your current IP address then only can they block website categories according to your preference. Besides this, they have logging facility for you to inspect a list of malware domains (attempted to be) visited by your home network.
Next, follow the instructions on OpenDNS support page or if you prefer to follow my guide, download the OpenDNS Root CA (file name Cisco_Umbrella_Root_CA.cer) from the support page and continue reading below for instructions on how to install into Windows.
Then, choose either to add certificate for all users or current user only.
To add the certificate for all users on the computer:
- Open the Microsoft Management Console by running
mmc - File > Add/Remove Snap-in
- Add Certificates (Local Computer)
- Right click on Trusted Root Certification Authorities > Certificates
- All Tasks > Import
- Select the
Cisco_Umbrella_Root_CA.cerfile that you have downloaded - Next all the way until completion
To add the certificate for current user on the computer:
- Open the Certificate Manager by running
certmgr.msc - Right click on Trusted Root Certification Authorities > Certificates
- All Tasks > Import
- Select the
Cisco_Umbrella_Root_CA.cerfile that you have downloaded - Next all the way until completion
Test the solution
Restart the web browser then visit the mock site again. You should now be seeing this: